FORM I-130A – Supplemental Information for Spouse Beneficiary
As of April 2017, U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) requires U.S. citizens or lawful permanent residents (green card holders) who are petitioning their spouse for a green card, in addition to Form I-130, to add Form I-130A, Supplemental Information for Spouse and Beneficiary, to the visa petition packet.
This supplementary form gathers additional biographical information of the beneficiary spouse. According to the USCIS instructions, this form replaces the previously required Form G-325A, which both the sponsor and foreign applicant in a marriage-based green card application were expected to fill out and submit.
Applicant’s Residence History
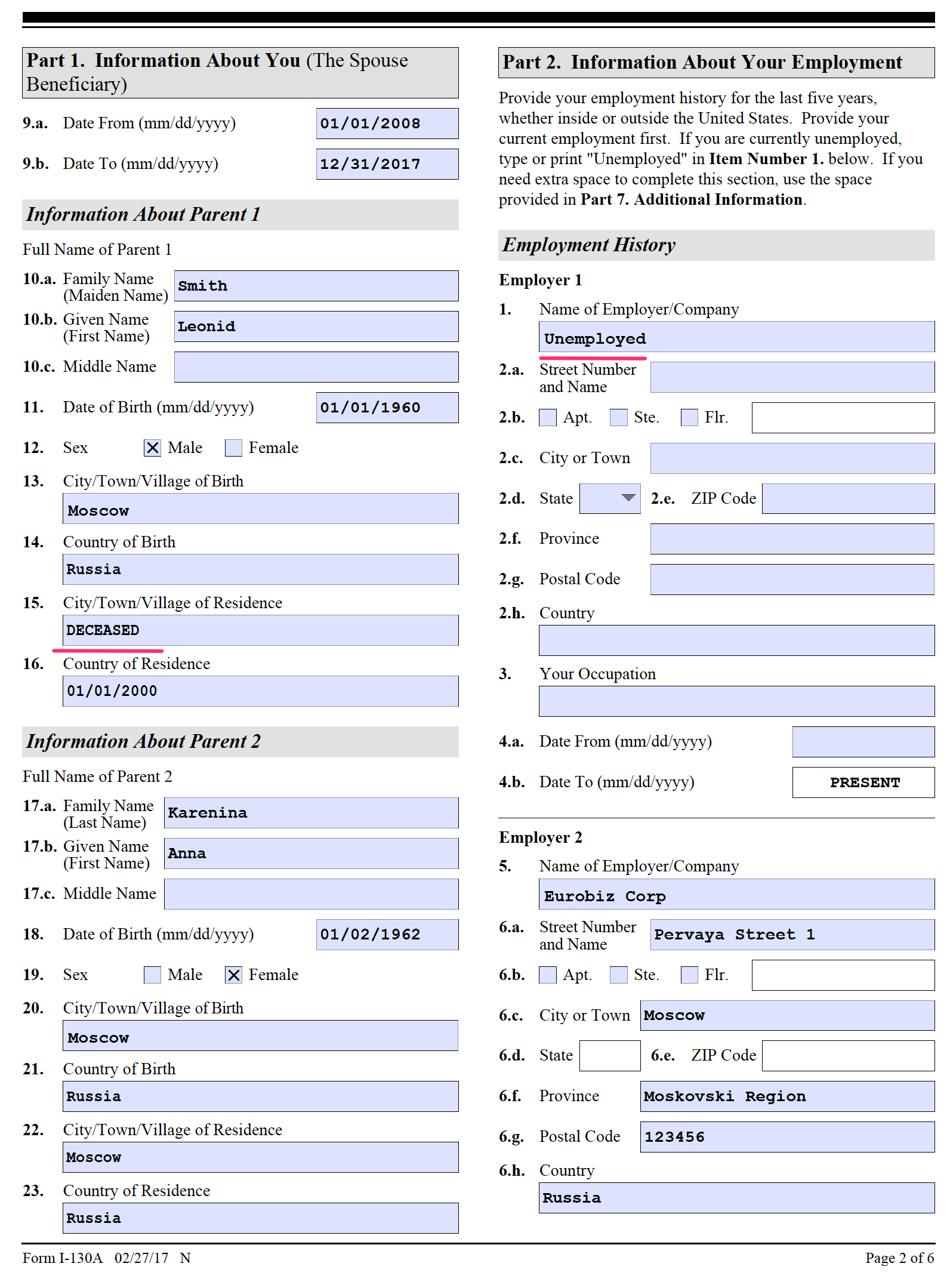
Part 1. Address History: There are three parts to this section. The first part requires the applicant to list all addresses for the last five years. List complete addresses (street and building numbers, city, state or province, country) and dates of residence at that address.
Key point to remember: Only disclose residences for the last five years. Do not list older residences (except last foreign residence).
NOTE: When compared with I-94 (admission record) and other forms, this information may disclose prior unlawful presence, unlawful status in the United States, or a failure to register a change of address. Background checks may disclose other addresses from arrest records, driver’s licenses, or previous immigration filings.
The second part requires the applicant to list the last address outside the United States EVEN if listed in the previous section. Again, list complete addresses (street and building numbers, city, state or province, country) and dates of residence at that address.
The third part asks to list parents. For parents, the information requested is fairly basic (name, date of birth, city and country of birth, city and country of residence). If the information is unknown (for example, a father’s identity is unknown, or a parent’s date of birth is unknown, indicate “unknown.” If a parent has passed away, write “deceased” and the year of death in the City and Country of Residence box. For the mother, her maiden family name should be entered.
Key point to remember regarding parents
Provide all information known. While there may be some risk of exposing an out-of-status parent or spouse, making a material misrepresentation while in the course of applying for an immigrant benefit is its own separate ground of inadmissibility.
Part 2 – Employment History
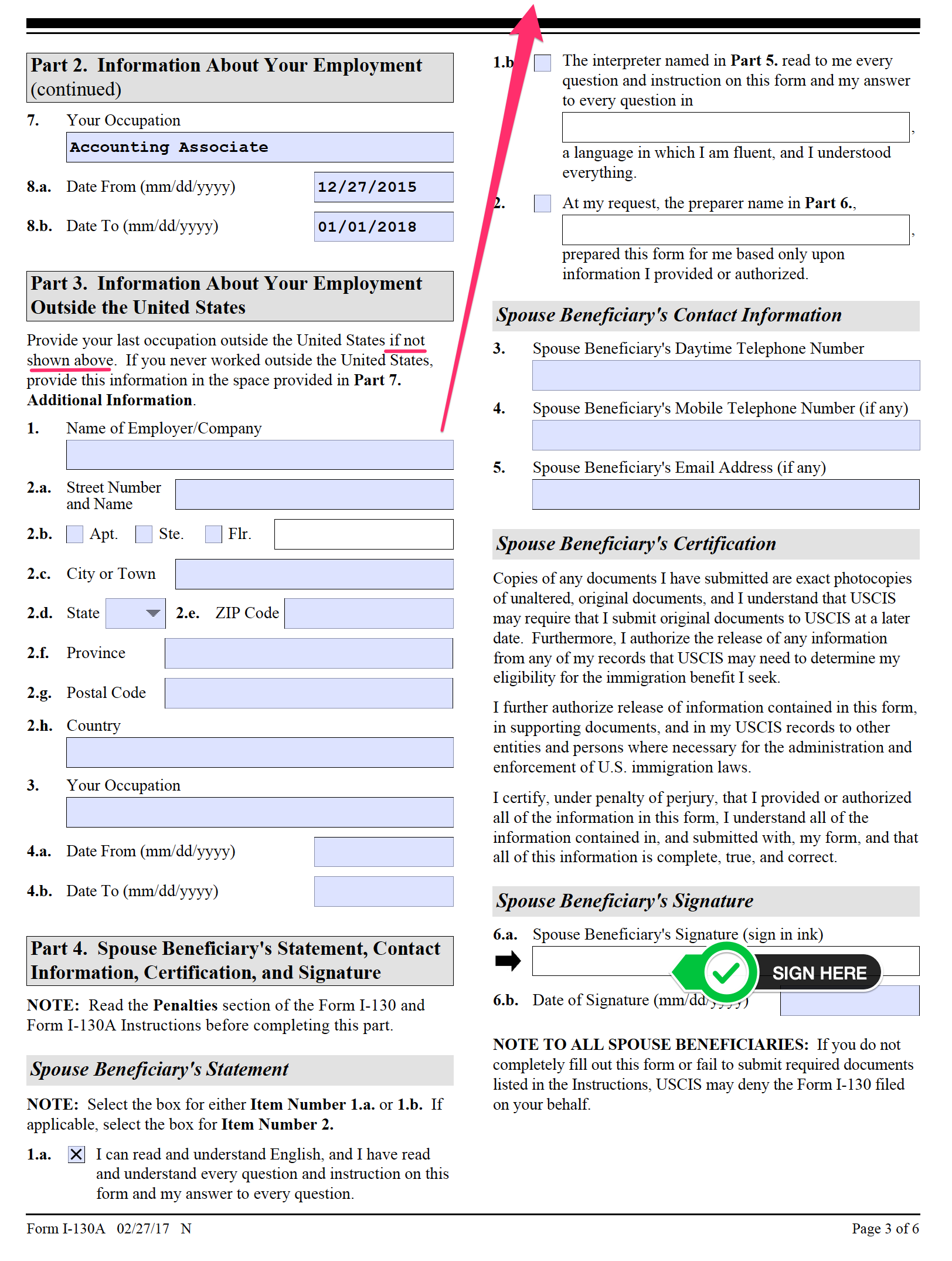
This part requires you to list all employment for the last five years. In addition to the employer’s name, this requires complete addresses (street and building numbers, city, state or province, country) and dates of employment with that employer.
NOTE: IF you require extra space to list all your employers then use the space provided in Part 7 – additional Information. See the example from Form I-130 on the proper format to provide additional information.
Part 3. Information About Your Employment Outside the United States
This part requires the beneficiary to list the last employment outside the United States IF not already listed in the previous section. In addition to the employer’s name, this requires complete addresses (street and building numbers, city, state or province, country) and dates of employment with that employ
Key points to remember:
* only disclose employment from the last five years. Do not list employment from more than five years ago (except last employment abroad).
* Remember when compared with the applicant’s I-94 (admission record) and other forms, this information may disclose unauthorized employment and status violations in the United States.









Thank you. it really helps. could you please guide which documents are required to file for mother. form i130 for Mother?
Thank You Kohinalaw. This cleared some of my confusions.